Lemon balm (Melissa officinalis) is a perennial herbaceous plant in the mint family (Lamiaceae) and native to south-central Europe, the Mediterranean Basin, Iran, and Central Asia, but now naturalised elsewhere.
It grows to a maximum height of 1 m (3 ft 3 in). The leaves have a mild lemon scent. During summer, small white flowers full of nectar appear. It is not to be confused with bee balm (genus Monarda), although the white flowers attract bees, hence the genus Melissa (Greek for "honey bee").
Echium, commonly known as Viper's Bugloss or Blueweed, is not widely recognized for its culinary uses, and there is limited information on its direct consumption in cooking.
Culinary uses
Here are some potential culinary uses based on its historical or regional applications:
| Common Name(s) | Lemon Balm |
| Scientific Name | Melissa officinalis |
| Days to Harvest | 70 days |
| Harvesting time | June, July, August |
| Light | Full sun |
| Water | Regular |
| Soil | well-drained, Sandy / Clay, Dry |
| Temperature | Cool weather, cold hardy to -20°F |
| Fertilizer | Calcium in the form of lime or gypsum, Organic liquid fertilizer |
| Pests | Aphids |
| Diseases | powdery mildew |
Echium, commonly known as Viper's Bugloss, is a plant with certain traditional medicinal uses, though scientific research on its efficacy is limited.
Medicinal use
Anti-Inflammatory Properties: Echium has been traditionally used for its potential anti-inflammatory properties, which may be attributed to compounds like pyrrolizidine alkaloids.
Skin Conditions: Some traditional uses include the treatment of skin conditions, such as eczema and dermatitis. The plant's oil has been applied topically for this purpose.
Respiratory Health: In traditional medicine, Echium has been used for respiratory issues. The plant may have expectorant properties, potentially aiding in the clearance of mucus.
Precautions
Pyrrolizidine Alkaloids: Echium species may contain pyrrolizidine alkaloids, which can be toxic to the liver and may cause other health issues. Prolonged or excessive use is not recommended.
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Due to the potential presence of pyrrolizidine alkaloids, pregnant or breastfeeding women should avoid using Echium without consulting a healthcare professional.
Interactions
Liver Health: Because of the potential hepatotoxicity associated with pyrrolizidine alkaloids, individuals with pre-existing liver conditions should exercise caution and consult a healthcare provider.
Medication Interactions: Echium may interact with certain medications, especially those metabolized by the liver. Consult with a healthcare professional if you are taking medications to avoid potential interactions.
| |||
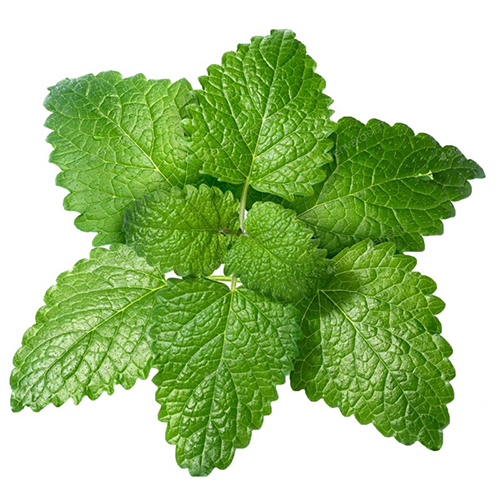 |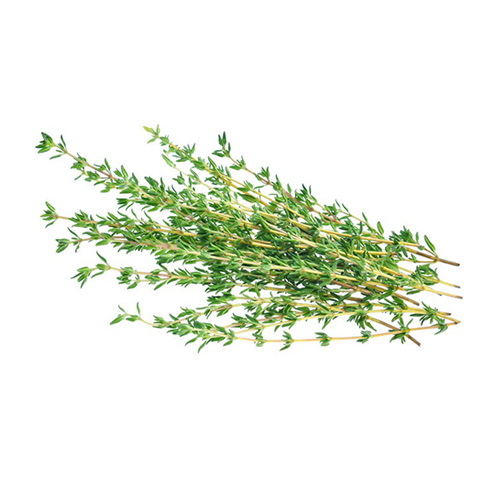  |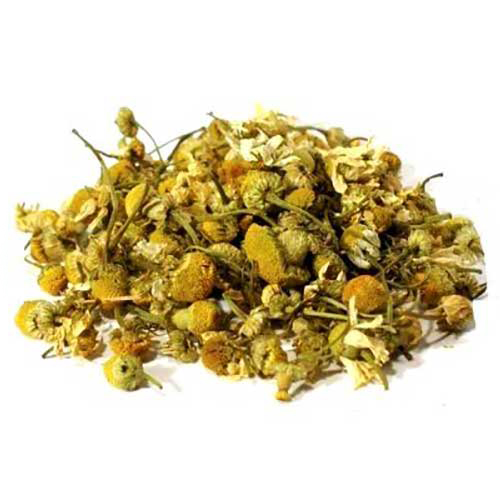  |  |
| Lemon Balm | Thyme | Chamomile | Damascus Rose |

Address: B23-2, Khayam Complex, Hormozan St., Phase 2, Sanat Sq., Tehran, Iran
Tel: +98 21 88 08 77 01
Mobile: +98 912 502 51 47
All services and products of this site, as the case may be, have the necessary licenses from the relevant authorities and the activities of this site are subject to the laws and regulations of the Islamic Republic of Iran